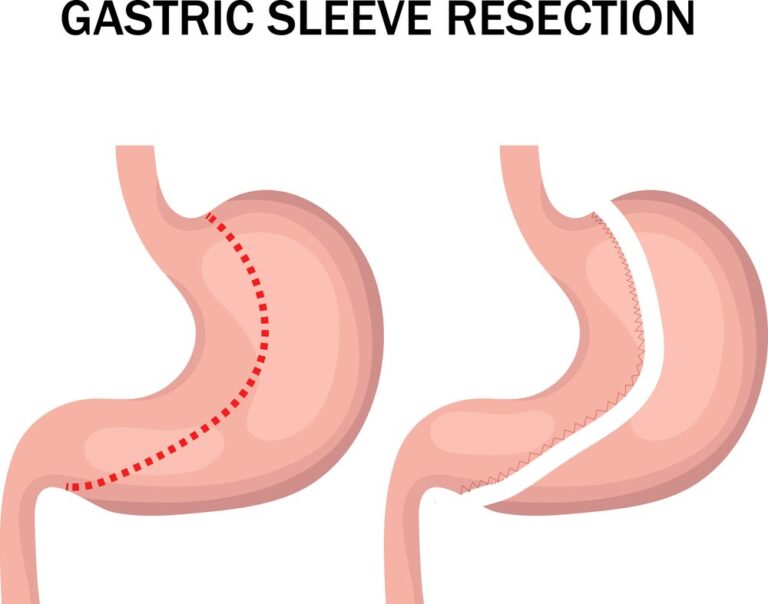
During a gastric sleeve surgery, also known as a sleeve gastrectomy, the number of incisions for gastric sleeve varies. Patients often wonder, “How many incisions for gastric sleeve?” While there is no fixed number, typically, multiple small incisions are made. These incisions, usually five or six in number, are small in size, ranging from 0.5 to 1 centimeter.
They serve as access points for the surgical instruments and laparoscope, allowing the surgeon to perform the procedure effectively. By removing a large portion of the stomach, a smaller sleeve-shaped stomach is created, aiding in weight loss.
Get a $1000 Off on Gastric Sleeve in Miami
How Many Incisions are Typically Made for Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
Typically, during a gastric sleeve surgery, several small incisions are made. The procedure is usually performed laparoscopically, which is a minimally invasive approach. The exact number of incisions can vary based on the surgeon’s technique and the patient’s specific needs. However, in most cases, four to six small incisions are made.
These incisions are typically around 0.5 to 1 centimeter in size and serve as entry points for the surgical instruments and a laparoscope. The laparoscope is a thin tube with a camera that allows the surgeon to visualize the surgical site on a monitor.
Using these small incisions, the surgeon will insert the necessary instruments to remove a large portion of the stomach, creating a sleeve-like shape. The remaining stomach is then closed using staples or sutures.
Where Are the Incisions Placed in Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
In gastric sleeve surgery, the incisions are typically placed in specific locations on the abdomen. The exact placement of the incisions can vary depending on the surgeon’s technique and the patient’s individual anatomy. However, there are common locations where the incisions are typically made during a laparoscopic gastric sleeve procedure.
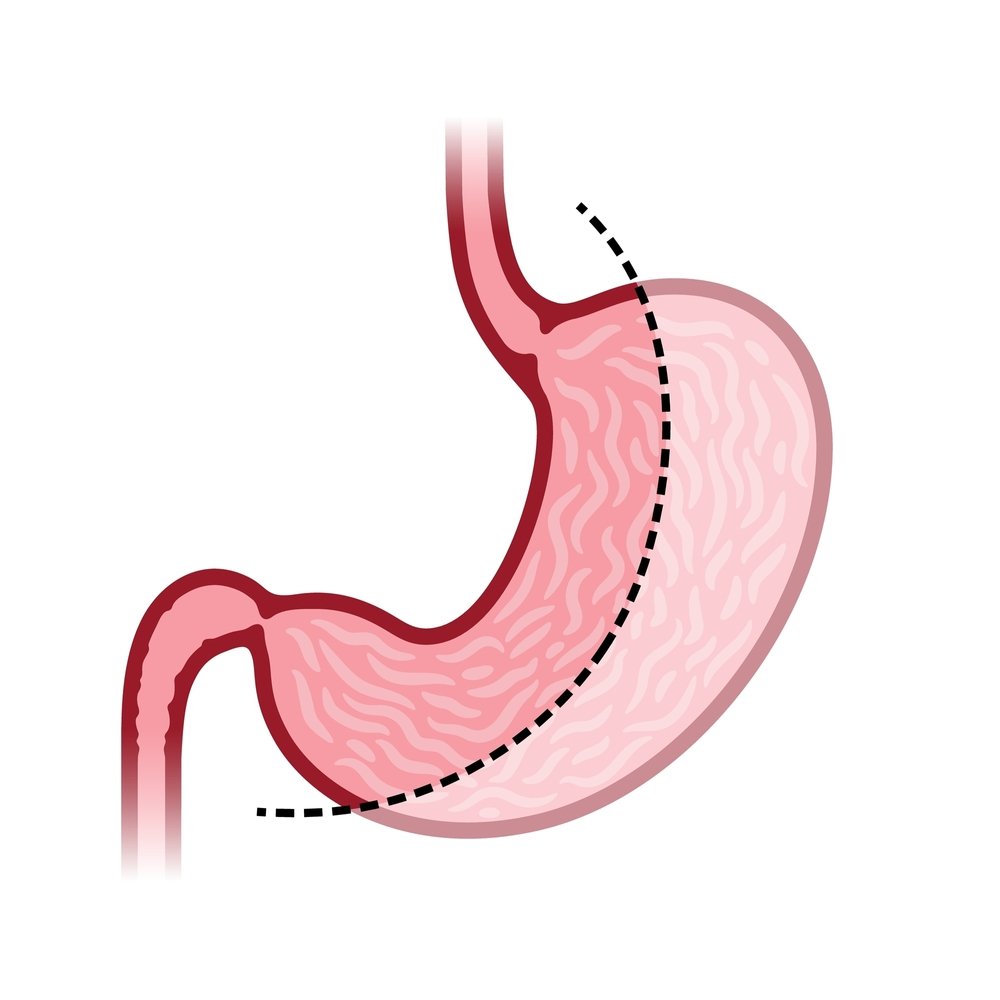
Here are the general locations where the incisions are often placed:
- Upper abdomen: One incision is usually made in the upper abdomen, slightly left of the midline. This incision is typically used for inserting the laparoscope, which allows the surgeon to visualize the surgical site.
- Left side of the abdomen: Several incisions are made on the left side of the abdomen. These incisions are used for inserting surgical instruments to perform the gastric sleeve procedure. The number of incisions can vary, typically ranging from three to five, depending on the surgeon’s preference and technique.
It’s important to note that the exact placement of the incisions should be discussed with your surgeon, as they will determine the best approach based on your individual circumstances.
Understanding the Laparoscopic Approach for Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Certainly! The laparoscopic approach for gastric sleeve surgery, also known as laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical technique. It involves making several small incisions in the abdomen, through which specialized surgical instruments and a laparoscope are inserted to perform the procedure.
Here’s a step-by-step overview of the laparoscopic gastric sleeve procedure:
- Anesthesia: You will be given general anesthesia to ensure you are asleep and pain-free throughout the surgery.
- Incisions: Typically, four to six small incisions (each about 0.5 to 1 centimeter) are made in specific locations on your abdomen. These incisions serve as access points for the surgical instruments and the laparoscope.
- Creation of the sleeve: The surgeon inserts a laparoscope, which is a long, thin tube with a camera and a light source, through one of the incisions. The laparoscope allows the surgeon to visualize the surgical area on a monitor. The abdomen is then inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create space for the surgical instruments.
- Removal of a portion of the stomach: Using specialized instruments inserted through the other incisions, the surgeon carefully removes a large portion of the stomach along the greater curvature. The remaining stomach is shaped into a sleeve-like tube, reducing its size significantly.
- Stapling or suturing: The surgeon closes the incisions made along the staple line using either staples or sutures to secure the newly created sleeve-shaped stomach.
- Closure and recovery: The surgical instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape. Small dressings may be applied, and you are moved to a recovery area.
The laparoscopic approach offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced scarring, less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and a lower risk of complications.
Considerations and Factors
When considering gastric sleeve surgery, there are several important factors and considerations to keep in mind:
| Factors and Considerations | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Weight loss goals | Gastric sleeve surgery is intended for individuals who have struggled with obesity and failed to lose weight through diet and exercise alone. Realistic weight loss goals should be established, understanding that the procedure is a tool that requires commitment to long-term lifestyle changes. |
| Health conditions | Pre-existing medical conditions and overall health will be assessed to determine candidacy for the surgery. Certain health conditions may influence the risks associated with the procedure or the potential benefits. |
| Surgical risks | Gastric sleeve surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries risks such as infection, bleeding, adverse reactions to anesthesia, blood clots, leaks or strictures in the sleeve, and other complications. Understanding and discussing these risks with the surgeon is important to make an informed decision. |
| Lifestyle changes | Significant lifestyle changes are necessary after gastric sleeve surgery. This includes adopting a new eating plan with smaller portion sizes and focusing on nutrient-dense foods, incorporating regular exercise, and engaging in long-term follow-up with healthcare professionals for successful weight loss and maintenance. |
| Nutritional considerations | Post-surgery, the body’s ability to absorb nutrients may change. Dietary supplements, such as multivitamins or calcium, may be required to ensure proper nutrition. Following the recommended dietary guidelines provided by the healthcare team is crucial to maintaining good health. |
| Emotional and psychological factors | Obesity can be linked to emotional and psychological challenges. Addressing these factors before and after surgery is important for long-term success. Considerations such as counseling or support groups may be beneficial in managing these aspects. |
| Cost and insurance coverage | Gastric sleeve surgery can be costly. Checking with the insurance provider to determine coverage and understanding any out-of-pocket expenses is important. Additionally, considering the financial impact of follow-up care and necessary lifestyle changes is essential. |
Does the Number of Incisions Vary Based on the Patient?
Yes, the number of incisions made during gastric sleeve surgery can vary based on the patient’s individual anatomy and the surgeon’s technique. While there is a general range of incisions typically used, the specific number may be adjusted to accommodate factors such as the patient’s body habitus (body shape and size) and the surgeon’s preferences.

Some patients may require additional incisions if their anatomy or surgical needs dictate it. Conversely, in certain cases, the surgeon may be able to perform the procedure with fewer incisions if the patient’s anatomy allows for it. The goal is to ensure safe and effective access to the surgical site while minimizing the invasiveness of the procedure.
Are There Any Alternative Techniques with Fewer Incisions?
Yes, there are alternative techniques for gastric sleeve surgery that can be performed with fewer incisions or even a single incision. These techniques aim to further minimize the invasiveness of the procedure and potentially reduce scarring. Here are two alternative approaches:
- Single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS): SILS, also known as single-port or single-site surgery, involves performing the entire gastric sleeve procedure through a single small incision, typically made in the belly button. Specialized instruments are used that can be inserted through the same incision. This technique offers the advantage of potentially leaving a single, well-hidden scar.
- Robotic-assisted gastric sleeve surgery: Robotic-assisted surgery utilizes robotic arms controlled by the surgeon to perform the procedure. It allows for increased precision and dexterity compared to traditional laparoscopic instruments. With robotic surgery, the number of incisions can vary depending on the specific robotic platform used, but it often involves fewer incisions than traditional laparoscopy.
It’s important to note that these alternative techniques may not be suitable for every patient. Factors such as the patient’s anatomy, previous surgeries, and surgeon’s expertise may influence the feasibility and appropriateness of these approaches. Your surgeon will evaluate your individual case and determine the most appropriate technique for you.
How Surgeons Determine the Optimal Number of Incisions
Surgeons determine the optimal number of incisions for gastric sleeve surgery based on several factors, including the patient’s anatomy, body habitus (body shape and size), surgical requirements, and the surgeon’s expertise and preferred technique. Here’s an overview of how surgeons typically assess and determine the number of incisions:
| Factors Considered for Determining Incision Number in Gastric Sleeve Surgery |
|---|
| Patient Anatomy and Body Habitus |
| Surgeon’s Expertise and Preferred Technique |
| Preoperative Evaluation (BMI, Abdominal Anatomy, Prior Surgeries, Health Considerations) |
| Surgical Plan and Technique Selection |
| Visualization and Access Requirements |
| Patient-Specific Factors (e.g., Size, Anatomy) |
| Surgeon Experience and Preference |
Please note that this table summarizes the factors that surgeons consider when determining the number of incisions for gastric sleeve surgery.
Recovery and Scarring
Recovery and scarring are important considerations when undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Here’s an overview of what you can expect in terms of recovery and scarring:
Recovery:
- Hospital stay: After the surgery, you will typically remain in the hospital for a few days to monitor your recovery. The exact duration may vary depending on individual circumstances and the surgeon’s recommendations.
- Pain management: You may experience some pain or discomfort in the days following the surgery. Your healthcare team will provide pain medication to manage any discomfort during the recovery period.
- Gradual return to normal activities: You will need to gradually reintroduce activities into your routine. Your surgeon will provide specific guidelines regarding physical activity, lifting restrictions, and the resumption of work or other daily activities.
- Dietary changes: Following gastric sleeve surgery, you will need to adhere to a specific post-operative diet plan. Initially, this may involve a liquid or pureed diet, gradually progressing to soft foods and eventually solid foods. It’s crucial to follow your surgeon’s dietary recommendations for optimal healing and weight loss.
- Long-term follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare team are essential for monitoring your progress, adjusting your diet and medications, and providing ongoing support for long-term success.
Scarring:
- Incision size and placement: The incisions made during gastric sleeve surgery are typically small (around 0.5 to 1 centimeter). The placement of the incisions aims to minimize scarring and make them as discreet as possible.
- Scar healing: Over time, the incisions will heal and the scars will gradually fade. The exact timeline for scar healing can vary among individuals, but it generally takes several months to a year for scars to become less noticeable.
- Scar care: Your surgeon may provide instructions on scar care, such as keeping the incision sites clean and dry, avoiding direct sunlight exposure, and using topical scar treatments. Following these recommendations can help optimize scar healing.
- Individual variability: Scarring can vary from person to person based on factors such as skin type, genetics, and individual healing processes. While most scars will become less prominent over time, some individuals may have a more noticeable scar appearance.
How Long Does It Take for Incision Scars to Heal?
The healing process and timeline for incision scars can vary among individuals. While it’s difficult to provide an exact timeframe as it depends on various factors, here is a general overview of the stages of scar healing:
- Initial healing (1-2 weeks): During the first week or two after surgery, the incision scars will go through the initial healing phase. The incisions may be red, raised, and tender during this time. The body begins the process of closing the incisions and forming scar tissue.
- Maturation (2-6 months): Over the next few months, the scars will gradually improve in appearance. They may become lighter in color, flatten out, and become less noticeable. It’s common for scars to feel itchy or sensitive during this stage, but it’s important to resist the urge to scratch or pick at them to avoid complications.
- Long-term remodeling (6 months to 1 year or longer): The final stage of scar healing involves long-term remodeling. During this period, the scars continue to refine and fade. They may become smoother, less raised, and blend more naturally with the surrounding skin. However, it’s important to note that individual variation exists, and complete scar maturation can take longer for some individuals.
Several factors can influence the healing process and the appearance of scars, including:
- Individual healing capacity: Each person’s body has its unique healing abilities, which can impact scar formation and the healing timeline.
- Genetics: Genetic factors play a role in how scars form and fade.
- Wound care: Following proper wound care instructions provided by your surgeon can promote optimal healing and minimize complications.
- Sun exposure: Protecting the incision scars from excessive sun exposure during the healing process can help prevent hyperpigmentation and further scarring.
- Lifestyle factors: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including good nutrition, hydration, and avoiding smoking, can positively impact the healing process.
Minimizing and Managing Incision Scarring
Minimizing and managing incision scarring is a common concern for many individuals. While complete prevention of scars is not possible, there are several strategies you can follow to help minimize and manage incision scarring:
- Follow proper wound care: It’s important to adhere to the wound care instructions provided by your surgeon. This typically involves keeping the incision sites clean and dry, changing dressings as instructed, and avoiding activities that could strain or disrupt the incisions during the initial healing phase.
- Protect from sun exposure: Sun exposure can cause scars to darken and become more noticeable. Protect your incision scars from direct sunlight by keeping them covered or applying sunscreen with a high SPF.
- Massage the scars: Gently massaging the incision scars once they have fully closed and are no longer scabbing can help break down scar tissue and promote better healing. Consult your surgeon for specific instructions on scar massage techniques.
- Use silicone gel or sheets: Silicone-based products, such as silicone gel or sheets, can be applied to the incision scars to help flatten and soften them. These products are available over-the-counter and may be recommended by your surgeon.
- Topical creams or ointments: Certain topical creams or ointments containing ingredients like vitamin E, aloe vera, or onion extract may be beneficial in managing scars. However, it’s important to consult your surgeon before using any specific product to ensure its safety and efficacy.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can impair the healing process and increase the risk of complications, including poor scar formation. It’s advisable to avoid smoking or using any tobacco products during the healing period.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate hydration, can support optimal healing and skin health.
- Give it time: Scar healing is a gradual process that takes time. Be patient and give your body the time it needs to heal and for scars to mature and fade naturally.
If you have concerns about incision scarring, it’s best to discuss them with your surgeon. They can provide personalized advice, recommend specific products or techniques, and address any specific concerns you may have.
References:
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. (2021). Sleeve Gastrectomy. Retrieved May 10, 2023