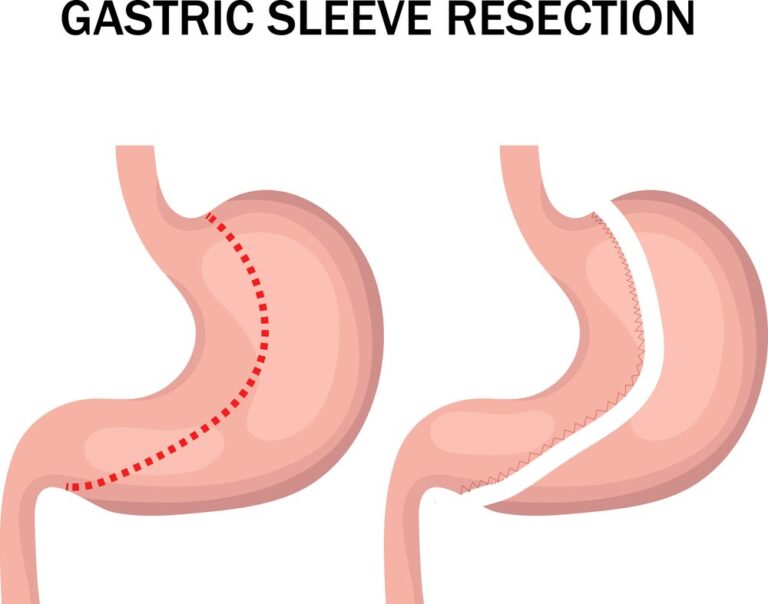
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, is a surgical weight loss procedure for individuals with severe obesity. It involves removing a large portion of the stomach to create a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach, which restricts food consumption and promotes weight loss.
Following gastric sleeve surgery, it’s essential to make dietary changes to support healing and encourage sustained weight loss. A common question that arises is whether one can eat ramen noodles after gastric sleeve surgery. In this article, we’ll delve into the feasibility of incorporating ramen noodles into a post-operative diet and provide alternative meal plan suggestions for maintaining health and nutrition after undergoing gastric sleeve surgery.
Get a $1000 Off on Gastric Sleeve in Miami
The Challenges of Ramen Noodles After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Consuming ramen noodles after gastric sleeve surgery presents several challenges. The surgery reduces the stomach’s capacity, making it difficult to digest high-carbohydrate and high-sodium foods like ramen noodles. This can lead to discomfort, bloating, and dumping syndrome. Ramen noodles also lack nutritional value and can hinder weight loss efforts due to their high calorie content.
It is important for individuals who have undergone gastric sleeve surgery to explore alternative options that meet their dietary requirements and promote a healthy recovery.

Risks and Considerations When Eating Ramen Noodles After Gastric Sleeve
Consuming ramen noodles after gastric sleeve surgery poses certain risks and considerations that individuals should be aware of. Gastric sleeve surgery significantly reduces the stomach’s size and alters the digestive system, which can affect how the body processes and tolerates certain foods. When it comes to ramen noodles, there are several factors to consider:
- Difficulty in digestion: Ramen noodles are typically high in carbohydrates, which can be challenging for the smaller stomach to digest effectively. This can lead to discomfort, bloating, and potential digestive issues.
- High sodium content: Ramen noodles are known for their high sodium content, which can be problematic for individuals who have undergone gastric sleeve surgery. Excessive sodium intake can cause fluid retention, high blood pressure, and other health complications.
- Lack of nutritional value: Ramen noodles are often processed and lack essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber. After gastric sleeve surgery, it is crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods that support healing, weight loss, and overall health.
- Impact on weight loss: Ramen noodles are calorie-dense and can hinder weight loss efforts, which are an important goal of gastric sleeve surgery. Consuming foods with high calorie content can impede progress and compromise the desired outcomes of the surgery.
- Potential dumping syndrome: Dumping syndrome is a condition that may occur after gastric sleeve surgery, where food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine. This can result in symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness. Foods high in carbohydrates and sodium, like ramen noodles, can trigger or worsen dumping syndrome symptoms.
Considering these risks and considerations, it is advisable for individuals who have undergone gastric sleeve surgery to prioritize foods that are easier to digest, lower in carbohydrates and sodium, and higher in nutritional value. This can help support the healing process, optimize weight loss, and ensure long-term success in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance on dietary choices and modifications after gastric sleeve surgery.
Get a $1500 Off on Gastric Bypass Surgery Miami
Post-Surgery Dietary Guidelines and Recommendations
In the journey towards recovery after surgery, proper nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting the healing process and restoring optimal health. Following surgery, the body undergoes various physiological changes, and adhering to post-surgery dietary guidelines can significantly contribute to a successful recovery.
Importance of Post-Surgery Dietary Guidelines
Proper nutrition following surgery offers numerous benefits. It helps in:
- Promoting wound healing and tissue repair.
- Reducing the risk of infection and complications.
- Boosting the immune system.
- Enhancing energy levels and preventing fatigue.
- Supporting overall recovery and rehabilitation.
- Improving outcomes and reducing the length of hospital stays.
Post-Surgery Dietary Guidelines
After surgery, your body needs time to heal and adjust. Following the recommended post-surgery dietary guidelines can aid in a smooth recovery. The guidelines may vary depending on the type of surgery and individual circumstances. Here are the general dietary recommendations for each phase of the recovery process:
- Early Recovery Phase: During the early recovery phase, when your body is still adjusting, it’s important to start with a gradual transition from liquids to solid foods. Here are the dietary guidelines for this phase:
- Clear Liquid Diet: In the initial stages, a clear liquid diet is typically recommended. This includes water, broth, herbal tea, and clear fruit juices without pulp. These fluids provide hydration and some essential nutrients while being gentle on the digestive system.
- Soft and Pureed Foods: As your body tolerates clear liquids, you can gradually introduce soft and pureed foods. Examples include mashed potatoes, yogurt, smoothies, well-cooked vegetables, and blended soups. These foods are easier to digest and provide additional nutrients.
- Mid-Recovery Phase: As your recovery progresses, you can gradually transition to a more solid food diet. Here are the dietary guidelines for this phase:
- Transitioning to Solid Foods: Start incorporating soft, easily chewable foods into your meals. This may include cooked vegetables, lean proteins, soft fruits, and whole grains. Chewing your food thoroughly and taking smaller, frequent meals can help ease digestion.
- Incorporating Nutrient-Dense Foods: Focus on including nutrient-dense foods in your diet to support the healing process. These include lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. These foods provide a rich array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants necessary for recovery.
High Carbohydrate and Calorie Content of Ramen Noodles
Ramen noodles, a popular staple in many households and college dorms, are beloved for their convenience and affordability. However, it’s important to be aware of their nutritional composition, particularly their high carbohydrate and calorie content. While ramen noodles can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, excessive consumption may have implications for your health.
Ramen noodles are typically made from wheat flour, water, salt, and other ingredients. They are often pre-cooked, dehydrated, and packaged with seasoning packets. While they may seem like a quick and easy meal option, it’s essential to understand the nutritional aspects.
High Carbohydrate Content
One of the primary components of ramen noodles is carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are a valuable source of energy for the body, but it’s important to consume them in moderation and choose complex carbohydrates over refined ones. Ramen noodles, however, are predominantly made from refined wheat flour, which lacks the fiber and nutrients found in whole grains.
High Calorie Content
Ramen noodles are also relatively high in calories. The seasoning packets that often accompany the noodles can add extra flavor but also increase the calorie content. Additionally, the noodles themselves are typically fried or deep-fried during the manufacturing process, which further increases their calorie content.
On average, a single serving of ramen noodles can provide around 188 to 400 calories, depending on the brand and specific ingredients. These calories primarily come from carbohydrates and fats. Consuming excessive calories without considering overall dietary balance and physical activity levels can lead to weight gain and associated health issues.
Nutritional Considerations
While ramen noodles may not be the healthiest choice, there are ways to make them more nutritious:
- Portion Control: Be mindful of serving sizes and avoid eating multiple packets of ramen noodles in one sitting. Stick to a single serving and balance it with other nutrient-rich foods.
- Enhance with Vegetables and Protein: Add vegetables like spinach, carrots, mushrooms, or bell peppers to increase the nutritional value of your ramen noodles. Consider adding lean protein sources like chicken, tofu, or shrimp for a more balanced meal.
- Homemade Broth: Instead of relying solely on the seasoning packet, prepare a homemade broth using low-sodium options or choose healthier broth alternatives. This reduces the sodium content and allows for better control over the flavor and ingredients.
- Choose Whole Grain Options: Some brands offer ramen noodles made from whole grain or alternative flours. Opt for these varieties when available, as they contain more fiber and nutrients compared to traditional refined flour options.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your hunger and fullness cues while consuming ramen noodles. Eating slowly and savoring each bite can help you feel satisfied with a smaller portion.
Remember, while ramen noodles can be enjoyed occasionally, it’s essential to prioritize a well-rounded and balanced diet. Incorporate a variety of whole foods, including lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to ensure you meet your nutritional needs. Regular physical activity and hydration are also crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Digestive Issues and Discomfort Associated with Ramen Noodles
Ramen noodles, a popular convenience food, are known for their quick preparation and affordability. However, despite their widespread appeal, consuming ramen noodles may lead to various digestive issues and discomfort. It’s important to understand the potential implications on your digestive health and make informed choices regarding their consumption.
| Digestive Concern | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of Fiber | Ramen noodles are typically low in fiber due to being made from refined wheat flour. This can lead to slower bowel movements, constipation, and long-term digestive problems. | Increase fiber intake by adding fiber-rich ingredients such as vegetables, legumes, and leafy greens. Drink plenty of water to aid digestion. |
| High Sodium Content | The high sodium content, especially in the seasoning packets, can cause water retention, bloating, increased blood pressure, and disrupt the balance of beneficial gut bacteria. | Choose ramen options with lower sodium content. Maintain a balanced diet with variety of whole foods. |
| Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) | Some ramen noodles contain MSG, which can cause bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in sensitive individuals. | Read labels and choose ramen options that do not contain MSG or other potentially problematic additives. |
| Poor Nutritional Profile | Ramen noodles often lack essential nutrients, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies and impaired digestive function. | Enhance nutritional value by incorporating other wholesome ingredients. Seek healthier alternatives such as whole grain noodles or homemade recipes. |
| Overall Digestive Health | Regular consumption of ramen noodles can contribute to various digestive issues and discomfort. | Moderation in consumption. Maintain a balanced diet and hydration. Seek medical advice if consistent digestive issues occur. |
Please note that the strategies listed in the table are not exhaustive, and individual health needs may vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Recommended Alternatives to Ramen Noodles After Gastric Sleeve
After undergoing gastric sleeve surgery, it’s important to make conscious choices about the foods you consume to support your recovery and maintain a healthy lifestyle. While ramen noodles may be a popular option for some, they are often high in carbohydrates and lack the necessary nutrients for post-surgery dietary needs. Here are some recommended alternatives to consider:
- Vegetable Noodle Options: Instead of traditional ramen noodles, opt for vegetable-based noodles that are lower in carbohydrates and higher in fiber. Vegetable noodles can be made from zucchini (zoodles), sweet potatoes (sweet potato noodles), or butternut squash (squash noodles).
- Shirataki Noodles: Shirataki noodles are a low-calorie, low-carbohydrate option that can be used as a substitute for ramen noodles. These noodles are made from konjac yam root and are virtually calorie-free.
- Cauliflower Rice: Cauliflower rice is an excellent alternative to traditional rice or noodles. It is low in carbohydrates and provides a good amount of fiber and essential nutrients. Cauliflower rice can be used as a base for stir-fries, as a side dish, or even in soups, allowing you to enjoy a satisfying meal without the excessive carbohydrates.
- Protein-Rich Options: After gastric sleeve surgery, it’s essential to prioritize protein intake to support healing and maintain muscle mass. Consider incorporating protein-rich alternatives to ramen noodles, such as:
- Lean meats: Choose grilled, baked, or broiled chicken, turkey, or fish as a protein source.
- Tofu: This plant-based protein option can be marinated and added to stir-fries or used as a topping in soups.
- Eggs: Hard-boiled eggs or scrambled eggs can provide a good source of protein for your meals.
- Broth-Based Soups with Vegetables and Protein: Instead of relying on ramen noodles for a comforting soup, create your own broth-based soups using low-sodium broths or homemade stocks. Include a variety of vegetables for added nutrients and flavor. Add protein sources such as shredded chicken, lean meat, or tofu to make the soup more filling and balanced.
- Customized Stir-Fries: Prepare customized stir-fries using a combination of colorful vegetables, lean proteins, and flavorful sauces. Use cauliflower rice, zucchini noodles, or shirataki noodles as a base and add your choice of protein and vegetables. Stir-frying allows for versatility in ingredients and portion control.
- Quinoa or Whole Grain Options: If you’re looking for a more substantial and nutritious alternative, consider incorporating quinoa or whole grain options like brown rice, whole wheat pasta, or whole grain couscous. These choices provide more fiber and nutrients compared to traditional ramen noodles.
Remember to follow your surgeon’s dietary guidelines and consult with a registered dietitian who specializes in post-gastric sleeve nutrition. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and help you develop a well-balanced meal plan that promotes your health and recovery.
Healthy and Nourishing Meal Options
After undergoing gastric sleeve surgery or simply aiming to adopt a healthier lifestyle, choosing nutritious meals is essential for overall well-being. Here are some healthy and nourishing meal options that provide a balance of nutrients and support your dietary goals:
| Meal | Key Ingredients | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Grilled Chicken Breast with Roasted Vegetables | Grilled chicken breast, broccoli, bell peppers, carrots | High in protein, low in carbohydrates, rich in essential nutrients |
| Baked Salmon with Quinoa and Steamed Asparagus | Salmon, quinoa, asparagus | Provides omega-3 fatty acids, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Vegetable Stir-Fry with Tofu and Brown Rice | Bell peppers, broccoli, snap peas, mushrooms, tofu, brown rice | Offers plant-based protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Spinach Salad with Grilled Shrimp and Quinoa | Spinach, grilled shrimp, quinoa, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers | Packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and protein |
| Turkey Chili with Black Beans and Sweet Potatoes | Ground turkey, black beans, tomatoes, sweet potatoes | High in protein, low in fat, good balance of carbohydrates and fiber |
| Lentil Soup with Whole Grain Bread | Lentils, vegetables, low-sodium broth, whole grain bread | High in fiber and plant-based protein |
| Greek Salad with Grilled Chicken or Chickpeas | Lettuce, tomatoes, cucumbers, onions, olives, feta cheese, chicken or chickpeas | Nutrient-rich, high in protein, fresh and flavorful |
Remember, these meals are nutritious and healthy when enjoyed as part of a balanced diet. Always consider your individual dietary needs and restrictions.