Experiencing frequent hunger, particularly feeling ‘Hungry Every 2 Hours After Gastric Sleeve Surgery‘, can be concerning. It’s crucial to comprehend the possible reasons behind this increased hunger post-surgery and discover effective strategies to manage it.
| Why Am I Feeling Hungry Every 2 Hours Post-Surgery? |
|---|
| 1. Healing and Adjustment Period |
| 2. Stomach Stretching |
| 3. Rapid Gastric Emptying |
| 4. Dietary Choices |
| 5. Portion Sizes and Meal Timing |
| 6. Hydration Levels |
| 7. Stress and Emotional Factors |
| 8. Metabolism and Individual Differences |
Get a $1000 Off on Gastric Sleeve in Miami
Understanding Gastric Sleeve Surgery and Its Impact on Appetite
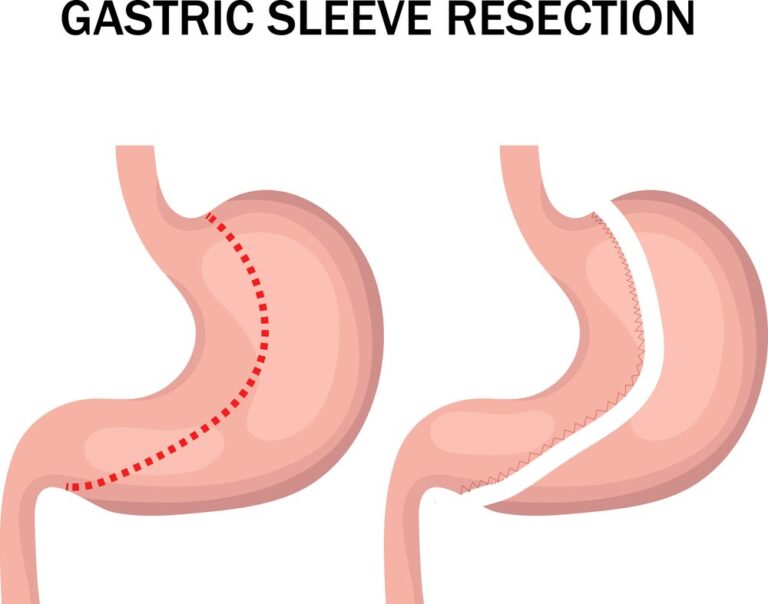
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, is a weight-loss procedure that involves removing a portion of the stomach to create a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach. This surgery has a significant impact on appetite and can help individuals achieve long-term weight loss. Here’s a closer look at how gastric sleeve surgery affects appetite:
- Reduction in Stomach Size: The primary mechanism behind gastric sleeve surgery is the reduction in stomach size. By removing a large portion of the stomach, the capacity for food intake is significantly reduced. The smaller stomach limits the amount of food that can be consumed during a meal, leading to feelings of fullness with smaller portions.
- Changes in Hormones: Gastric sleeve surgery can alter the production and regulation of certain hormones that influence appetite. The surgery affects the gut-brain communication, leading to changes in appetite-regulating hormones such as ghrelin, leptin, and peptide YY. These hormonal changes contribute to decreased hunger and increased feelings of fullness.
- Improved Satiety: With a smaller stomach size and hormonal changes, gastric sleeve surgery enhances feelings of satiety. This means individuals may feel satisfied with smaller meals, reducing the urge to eat frequently or excessively. The surgery promotes a sense of fullness, making it easier to control portion sizes and manage appetite.
- Reduction in Cravings: Many individuals who undergo gastric sleeve surgery experience a reduction in food cravings, especially for high-calorie and unhealthy foods. The changes in hormone levels and the smaller stomach size can help minimize cravings for certain foods, making it easier to adhere to a healthier diet.
- Behavioral Changes: Gastric sleeve surgery often requires individuals to make significant lifestyle changes, including adopting healthier eating habits and regular exercise. These behavioral modifications can positively impact appetite regulation. Following a balanced diet and engaging in physical activity can further enhance feelings of fullness and promote weight loss.

It is important to note that while gastric sleeve surgery can have a substantial impact on appetite, individual experiences may vary. Some individuals may still experience fluctuations in appetite or hunger, albeit reduced in intensity. Working closely with a healthcare team, including dietitians and support groups, can provide guidance on post-surgery dietary adjustments and effective appetite management strategies.
How Gastric Sleeve Surgery Affects Hunger and Satiety
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, has a significant impact on hunger and satiety. Understanding these effects can help individuals manage their appetite and make informed choices after surgery. Here’s how gastric sleeve surgery affects hunger and satiety:
- Reduced Stomach Capacity: During the surgery, a large portion of the stomach is removed, creating a smaller stomach pouch. This reduction in stomach size limits the amount of food that can be consumed, leading to a feeling of fullness with smaller meals. The decreased stomach capacity helps control hunger by reducing the amount of food needed to satisfy appetite.
- Changes in Hormones: Gastric sleeve surgery alters the hormonal balance in the body, particularly affecting appetite-regulating hormones. The surgery leads to a decrease in the production of ghrelin, a hormone responsible for stimulating hunger. With lower levels of ghrelin, individuals experience reduced feelings of hunger.
- Improved Satiety Signals: The smaller stomach pouch created during the surgery sends signals to the brain that indicate fullness more quickly. This enhanced satiety response means individuals feel satisfied with smaller portions of food, promoting portion control and reducing the desire to eat more frequently.
- Slower Digestion: After gastric sleeve surgery, the food passes more slowly through the digestive system. This slower digestion rate allows for better nutrient absorption and helps maintain a feeling of fullness for a longer period. Slower digestion can also stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent rapid spikes and crashes that can trigger hunger.
- Psychological Changes: Gastric sleeve surgery can have psychological effects on hunger and satiety. Individuals may experience a shift in their perception of hunger and satisfaction with smaller amounts of food. This change can contribute to a healthier relationship with food and improved self-control.
- Lifestyle Modifications: To optimize the effects of gastric sleeve surgery on hunger and satiety, individuals are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits. This includes following a nutrient-dense diet, practicing mindful eating, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity. These lifestyle modifications support appetite control and weight management.
It is important to note that while gastric sleeve surgery has significant effects on hunger and satiety, individual experiences may vary. Factors such as dietary choices, emotional well-being, and lifestyle habits can influence appetite post-surgery.
The Difference Between Physical Hunger and Emotional Hunger
Understanding the distinction between physical hunger and emotional hunger is important for developing a healthy relationship with food. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between these two types of hunger:
| The Difference Between Physical Hunger and Emotional Hunger |
|---|
| Physical Hunger |
| – Bodily Sensations |
| – Gradual Onset |
| – Specific Physical Symptoms |
| – Satiety After Eating |
| – Nutrition-Focused |
| Emotional Hunger |
| – Mood-Driven |
| – Sudden Onset |
| – Cravings for Specific Foods |
| – Lack of Satiety |
| – Mindless Eating |
By recognizing and differentiating between physical and emotional hunger, you can make conscious choices about when and what to eat, fostering a healthier relationship with food and a better understanding of your body’s needs.
Importance of a Balanced Diet and Regular Exercise
Maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise are fundamental components of a healthy lifestyle. Both aspects play crucial roles in promoting overall well-being and reducing the risk of various health conditions. Here are the key reasons why a balanced diet and regular exercise are important:
Balanced Diet:
- Nutritional Adequacy: A balanced diet ensures that your body receives all the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals it needs to function optimally. It supports growth, development, and repair of tissues, as well as the proper functioning of organs and systems.
- Energy Levels: A well-balanced diet provides the energy required for daily activities. It helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and promoting sustained energy throughout the day.
- Weight Management: A balanced diet helps maintain a healthy weight. It includes appropriate portion sizes, a variety of nutrient-dense foods, and limits the intake of unhealthy fats, added sugars, and processed foods. By promoting weight management, a balanced diet reduces the risk of obesity and related health conditions.
- Disease Prevention: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients and antioxidants. These components can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers, and other health conditions.
- Digestive Health: A balanced diet supports good digestive health. Adequate fiber intake from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and supports a healthy gut microbiome.

Regular Exercise:
- Cardiovascular Health: Regular exercise strengthens the heart and improves cardiovascular health. It reduces the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke by improving circulation, lowering cholesterol levels, and maintaining healthy blood vessels.
- Weight Management: Physical activity helps burn calories, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent weight gain. It increases metabolism, builds lean muscle mass, and contributes to a more toned and fit physique.
- Mental Well-being: Exercise releases endorphins, neurotransmitters that promote feelings of happiness and reduce stress and anxiety. It can boost mood, alleviate symptoms of depression, and improve overall mental well-being.
- Bone and Muscle Health: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, or weightlifting, help build and maintain strong bones and muscles. Regular exercise can reduce the risk of osteoporosis and improve balance, coordination, and flexibility.
- Improved Sleep: Engaging in regular physical activity can promote better sleep quality. It helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, reduces insomnia symptoms, and promotes a deeper, more restorative sleep.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Exercise has been linked to improved cognitive function, memory, and attention span. It stimulates blood flow to the brain, enhances neuroplasticity, and reduces the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Combining a balanced diet with regular exercise creates a synergistic effect, maximizing the benefits for overall health and well-being. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to develop a personalized nutrition and exercise plan that suits your specific needs and goals.
Identifying Signs of Complications Post-Surgery
After undergoing surgery, it is crucial to be aware of potential complications and recognize the signs that may indicate a problem. Here are some common signs of complications post-surgery:
| Identifying Signs of Complications Post-Surgery |
|---|
| 1. Fever |
| 2. Persistent Pain |
| 3. Excessive Swelling or Redness |
| 4. Prolonged or Excessive Bleeding |
| 5. Wound Drainage |
| 6. Shortness of Breath |
| 7. Chest Pain |
| 8. Changes in Urination or Bowel Movements |
| 9. Persistent Nausea and Vomiting |
| 10. Worsening Symptoms |
Regular Follow-up and Consultation with Your Surgeon
After undergoing surgery, including gastric sleeve surgery, regular follow-up and consultation with your surgeon are essential for monitoring your recovery and ensuring optimal post-surgical care. Here’s why regular follow-up and consultation are important:
- Monitoring Healing Progress: Regular follow-up appointments allow your surgeon to assess the progress of your healing. They can evaluate the surgical incisions, check for signs of infection or complications, and ensure that your recovery is on track.
- Addressing Concerns and Complications: If you experience any concerning symptoms or complications, regular consultations provide an opportunity to discuss these issues with your surgeon. They can assess the situation, provide guidance, and offer appropriate interventions to manage any complications that may arise.
- Adjusting Treatment Plan: During follow-up appointments, your surgeon can review your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Monitoring Weight Loss Progress: For individuals who undergo gastric sleeve surgery for weight loss purposes, regular follow-up appointments allow your surgeon to track your weight loss progress.
- Addressing Nutritional Needs: Following gastric sleeve surgery, it’s important to maintain proper nutrition to support healing and prevent nutrient deficiencies. Your surgeon can assess your nutritional status during follow-up visits and refer you to a registered dietitian if necessary.
- Long-Term Care and Support: Regular follow-up and consultation with your surgeon establish a long-term relationship, ensuring ongoing care and support. They can provide guidance on managing long-term complications, offer strategies for weight maintenance, and address any concerns or questions you may have along your post-surgical journey.
- Continuity of Care: By attending regular follow-up appointments, you ensure continuity of care. Your surgeon has a comprehensive understanding of your surgical history, individual needs, and any specific considerations related to your procedure.
Remember to schedule and attend all recommended follow-up appointments as advised by your surgeon. These appointments are essential for monitoring your progress, addressing any issues promptly, and ensuring the best possible outcomes following surgery. Openly communicate with your surgeon, share any concerns, and actively participate in your post-surgical care to promote optimal healing and overall well-being.